gynecologic oncologists in Anantapur
Gynecologic cancer encompasses any malignancy that originates in a woman's reproductive system needing intervention of Best gynecologic oncologists in Anantapur. The five primary types of cancer that impact these organs include cervical, ovarian, uterine, vaginal, and vulvar cancers. Collectively, these conditions are classified as gynecologic cancer.
Gynecologic cancers needing Best gynecological cancer treatment in Anantapur originate in various locations within a woman's pelvic region, situated beneath the abdomen and between the hip bones. Additionally, there exists a sixth, exceedingly rare form of gynecologic cancer known as fallopian tube cancer. Each type of gynecologic cancer possesses distinct characteristics, including varying signs and symptoms, risk factors, and prevention methods. All women are susceptible to these cancers, with the likelihood of occurrence rising with age. Early detection of gynecologic cancers significantly enhances the effectiveness of treatment.
Factors aiding in cancer as per Gynecology specialist in Anantapur
Several factors may elevate the likelihood of developing gynecologic cancer
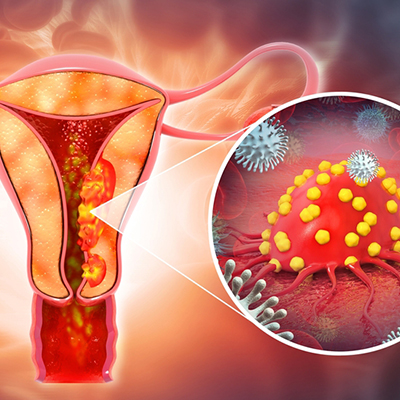
- Human papillomavirus (HPV) - Cancers of the cervix, vagina, and vulva are frequently associated with HPV, a prevalent sexually transmitted infection. Consequently, engaging in safe sex practices, such as condom use, is a crucial preventive measure. An HPV vaccine is available for girls and young women aged 11 to 26.
- Age - Advancing age is another recognized risk factor. For instance, the typical age at which a patient is diagnosed with uterine cancer is 63 years.
- Genetics - Approximately 10% of ovarian cancer cases are linked to a family history of the disease. Women with a mother, daughter, or sister who has had ovarian, Fallopian tube, or primary peritoneal cancer may consider genetic testing for BRCA1 and BRCA2 gene mutations, as these mutations can heighten the risk of ovarian cancer.
- Diethylstilbestrol Exposure - Certain gynecologic cancers have been correlated with in utero exposure to diethylstilbestrol, a synthetic estrogen that was prescribed to pregnant women from 1940 to 1971, prior to its classification as unsafe.
A woman's reproductive system is primarily focused on the uterus, also referred to as the womb, which includes the cervix. The ovaries are situated at the upper part of the uterus, while the vagina serves as the passageway connecting the uterus to the exterior of the body. The external genitalia are known as the vulva. Gynecologic cancers needing Best Gynecology Treatment in Anantapur arise from the accelerated proliferation and dissemination of abnormal cells within one of these reproductive organs. In contrast to other cancer types, such as breast or colon cancer, gynecologic cancers are relatively rare. For more information, consult Dr. G. P Sandhya Reddy.
